Shell and tube heat exchangers are a fundamental choice for industries that require reliable, high-temperature, and high-pressure heat transfer solutions. Known for their sturdy design, adaptability, and cost-effectiveness, these exchangers have become a standard in chemical processing, petroleum refining, power generation, and other demanding industries. In this blog, we’ll explore the working principles, structure, and advantages of shell and tube heat exchangers, along with their various types.
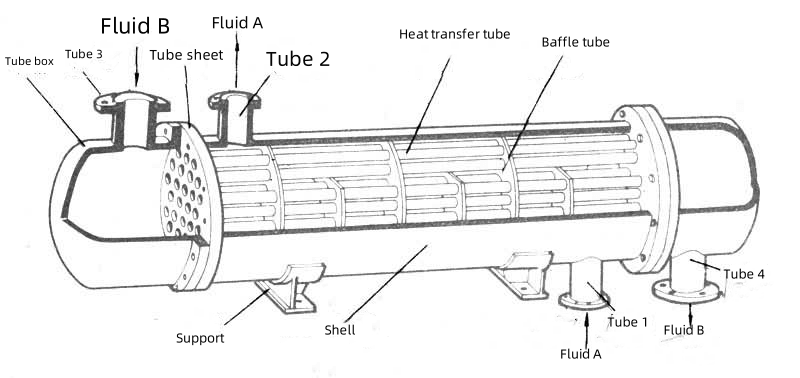
A shell and tube heat exchanger comprises a shell with multiple tubes inside it, facilitating heat exchange between two fluids across tube walls. This heat exchanger can handle pressures up to 4 MPa and temperatures above 200°C, making it ideal for high-stress applications.
Heat Exchange Process:
In the fixed-tube heat exchanger design, fluid A flows into the shell through an inlet, moves around the tubes, and exits through an outlet. Concurrently, fluid B flows through the tubes, exchanging heat with fluid A through the tube walls. If fluid A has a higher temperature than fluid B, heat transfers from A to B through the tube walls, and vice versa.
Shell and Tube Zones:
The area outside the tubes within the shell is known as the shell side, where shell-side fluid (fluid A) flows. The area inside the tubes is known as the tube side, where tube-side fluid (fluid B) flows. This division allows effective heat transfer and keeps the two fluids separated.
Enhanced Performance:
To increase efficiency, shell and tube heat exchangers may incorporate various configurations. Tubes can be straight or U-shaped, and materials such as finned or threaded tubes can be used. The tube arrangement can be triangular, square, or concentric, allowing for maximum tube density within the shell, which optimizes heat transfer area while meeting cleaning requirements and reducing resistance.
Key Components:
These heat exchangers consist of a tube bundle, shell, tube sheets, baffles, and optional flow dividers. Baffles direct fluid flow, increasing turbulence and enhancing heat transfer. These components also support the tubes and reduce vibration, ensuring the heat exchanger’s longevity and efficiency in demanding environments.
Advantages of Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
Shell and tube heat exchangers are robust, versatile, and relatively easy to manufacture, offering cost-effective heat exchange for a wide range of applications. Key benefits include:
Durability: The design is strong and withstands high temperatures and pressures.
Versatility: With options in materials and construction, shell and tube heat exchangers suit various applications and industries.
High Capacity: Ideal for processes requiring substantial heat exchange volumes.
Ease of Cleaning: While challenging to clean thoroughly, many shell and tube exchangers are designed for accessibility.
Types of Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
Several common designs enhance functionality for specific applications:
Fixed-Tube Heat Exchangers: The simplest and most common design; offers a compact setup but limited flexibility in thermal expansion.
Floating-Head Heat Exchangers: Allows tube bundles to expand and contract, reducing stress and extending the heat exchanger’s life.
U-Tube Heat Exchangers: Ideal for processes involving high temperature differentials, as the U-shaped tubes accommodate expansion.
Each type is suited to unique conditions, making shell and tube heat exchangers adaptable to a wide range of operational requirements.
Contact Us for Custom Solutions
At Wuxi Repicea, we provide a range of shell and tube heat exchangers, custom-designed to meet the needs of your industry. With our expertise, you can enhance efficiency and reliability in high-demand environments. Contact us today to learn more about our products or to discuss your unique requirements.
